Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology consists of several key components that work together to identify and track objects. Understanding these components is crucial to understanding how RFID systems work.
The following are the main components of RFID:
RFID Tags
RFID tags are the core element of an RFID system. They consist of two parts:
Microchip: The microchip stores a unique identifier for an item, along with any other information associated with that item. This data may include product details, historical records, and other relevant information.
Antenna: An antenna enables tags to communicate with RFID readers by transmitting and receiving radio waves. Antenna design varies depending on the type of RFID tag and its intended use.
RFID tags can be divided into two main categories:
Active Tags: These tags are self-powered (usually by batteries), enabling them to transmit signals over long distances (up to hundreds of meters). They are commonly used in applications requiring long-distance communication.
Passive tags: These tags have no power source and rely on energy emitted by the RFID reader to activate and transmit information. They typically have a shorter transmission distance (a few meters at most), but are less expensive and have a wider range of applications.
RFID Reader
An RFID reader is a device that transmits radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. They come in various forms, including handheld devices, fixed readers, and integrated systems.
The main functions of an RFID reader include:
Send signal: The reader emits radio waves to activate nearby RFID tags.
Receive Data: After the tag is activated, the reader captures the data transmitted by the tag and processes it for further use.
Data transmission: The reader then sends the collected data to a computer system or database for analysis and recording.
Antenna
Antennas are a key component for communication between RFID readers and tags. They can be integrated into the reader or used as a standalone component. The design and placement of the antenna significantly affect the communication range and performance of the RFID system.
Antennas can be designed for a variety of applications, including:
Near Field Communication: Suitable for short-range applications, such as access control.
Telecommunications: Used to track items over long distances, such as in supply chain management.
Middleware and Software
Middleware and software are crucial for managing the data collected by an RFID system.
These components include:
Data Processing: Software applications process the data received from RFID readers, enabling businesses to effectively analyze and utilize this information.
Integration: Middleware helps integrate RFID data with existing systems such as inventory management, supply chain systems, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
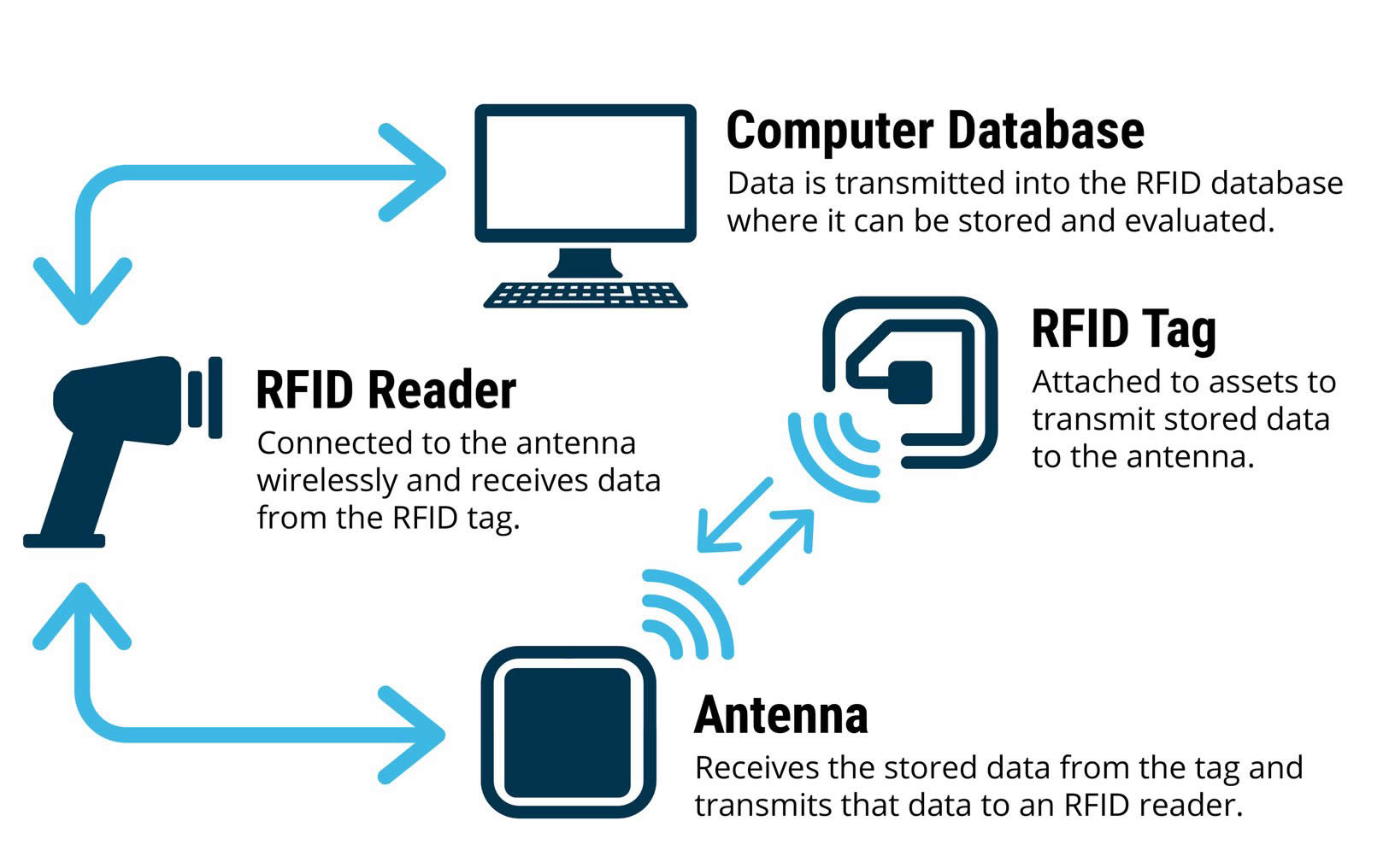
The main components of RFID—tags, readers, antennas, and software—work together to form a powerful object tracking and identification system. Understanding these components is crucial for businesses looking to effectively implement RFID technology.
HYDcard offers a comprehensive range of RFID products, designed to meet your specific needs. Our expertise in RFID technology can help you optimize operations, improve efficiency, and enhance process visibility. Contact us today to learn how our RFID solutions can empower your business!






